Heat of solidification |
您所在的位置:网站首页 › solidification › Heat of solidification |
Heat of solidification
|
During solidification, heat is released, which is called heat of crystallization or heat of solidification. It counteracts the external cooling. IntroductionThe hand warmer described in the article solidification conditions shows another phenomenon during the solidification of liquids (melts), which still needs an explanation. Obviously, heat is released during the crystallization of the hand warmer. This ultimately means that the hand warmer can be used as a heat source on cold winter days. In principle, this phenomenon of heating during solidification is not limited to the hand warmer. Ultimately, such a heat release takes place in every solidification process (crystallization). This effect will therefore be explained in more detail below. Pure substancesDuring the cooling of a melt, the expected temperature decrease is shown in the cooling curve. The temperature reduction is due to the continuously withdrawn heat energy from the melt. This leads to a reduction in the kinetic energy of the particles. When the solidification temperature (melting point) is reached, the kinetic energy of the particles has fallen to such an extent that the mutual attraction forces cause the particles to accumulate. With the creation of the lattice structure, however, the kinetic energy of the atoms decreases suddenly, as the particles show only a relatively small (vibrational) movement in the crystal compound. However, the difference in binding energies has not simply disappeared but has been converted into heat energy! In principle, this process can be imagined as an impact of a particle from the melt on the already solidified lattice structure, which then attaches itself to it. The impact also causes the grid structure to vibrate, which is equivalent to a (heat) energy input. This ultimately means a local temperature increase (note, that a higher vibrational movement means a higher temperature!). Such internal heat release during solidification is called heat of solidification. In the case of crystalline substances it is also referred to as crystallization heat. The heat of solidification released by crystalline materials is also called heat of crystallisation! The internal crystallization heat (“temperature increase”) released during solidification ultimately compensates for the external heat dissipation (“temperature reduction”). In fact, a permanent oscillation around the solidification temperature will be observed at the microscopic level. No heat is effectivly added to or removed from the solidifying substance during crystallization. The temperature therefore remains constant from a macroscopic point of view. 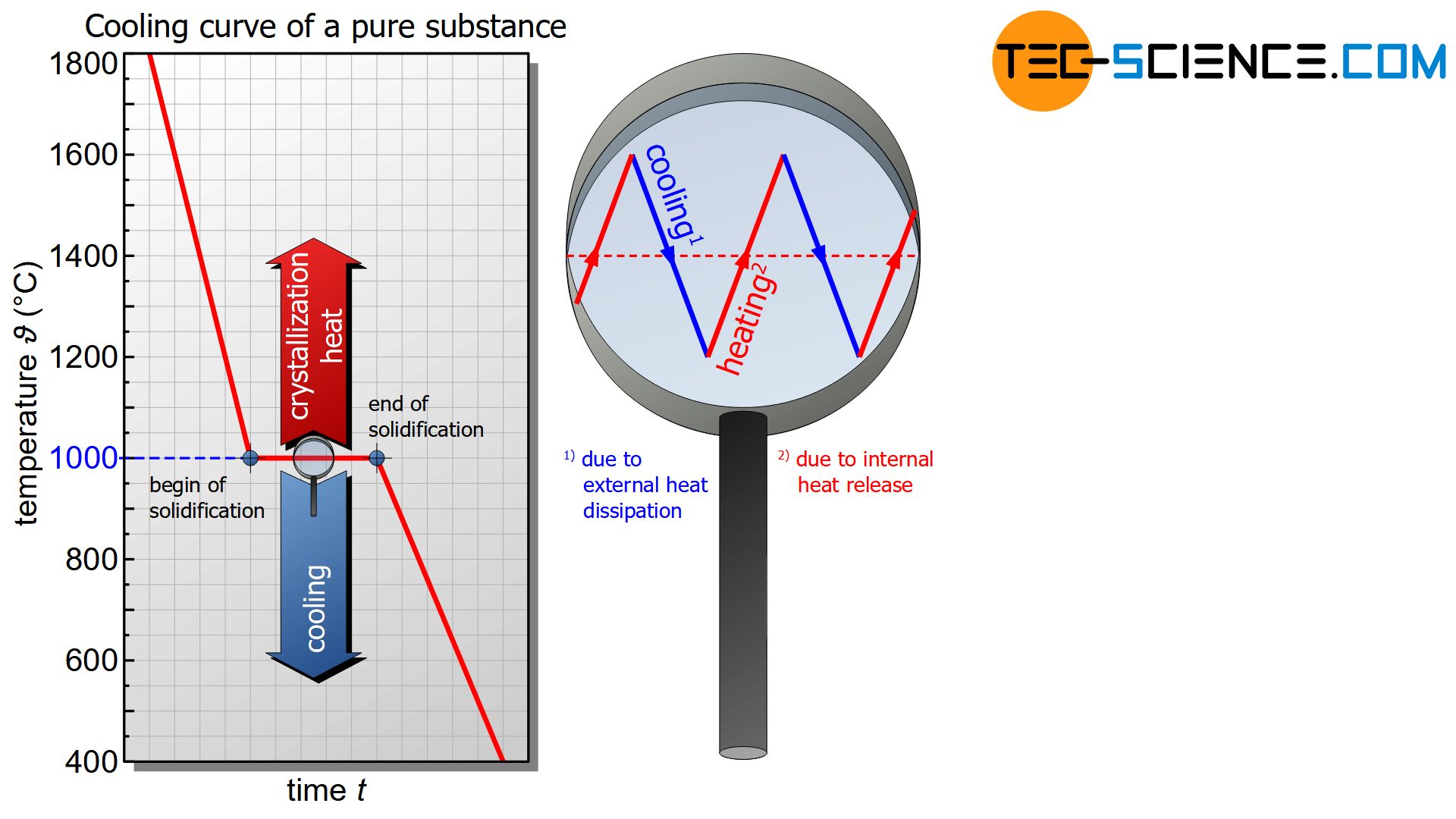 Figure: Cooling curve of a pure substance Figure: Cooling curve of a pure substance
This keeping constant of the temperature is also called thermal arrest and becomes noticeable in the cooling curve as a horizontal line. Only when all particles have adhered to the lattice structure and the solidification is finished, no more heat of crystallization can be released. From this point on, only the external heat dissipation becomes effective and the temperature finally begins to fall again. The effect that the temperature remains constant during solidification is a typical phenomenon of pure substances. During the solidification of pure substances, the temperature usually remains constant (thermal arrest)! MixturesIn principle, mixtures of substances also show such heat release during solidification. However, due to the mutual chemical influence of the substances, the heat of crystallisation can generally no longer fully compensate for cooling. As a result, the temperature decrease is no longer stopped completely but only slowed down. The cooling curve is only flatter during solidification. During the solidification of mixtures, the temperature decrease usually slows down! 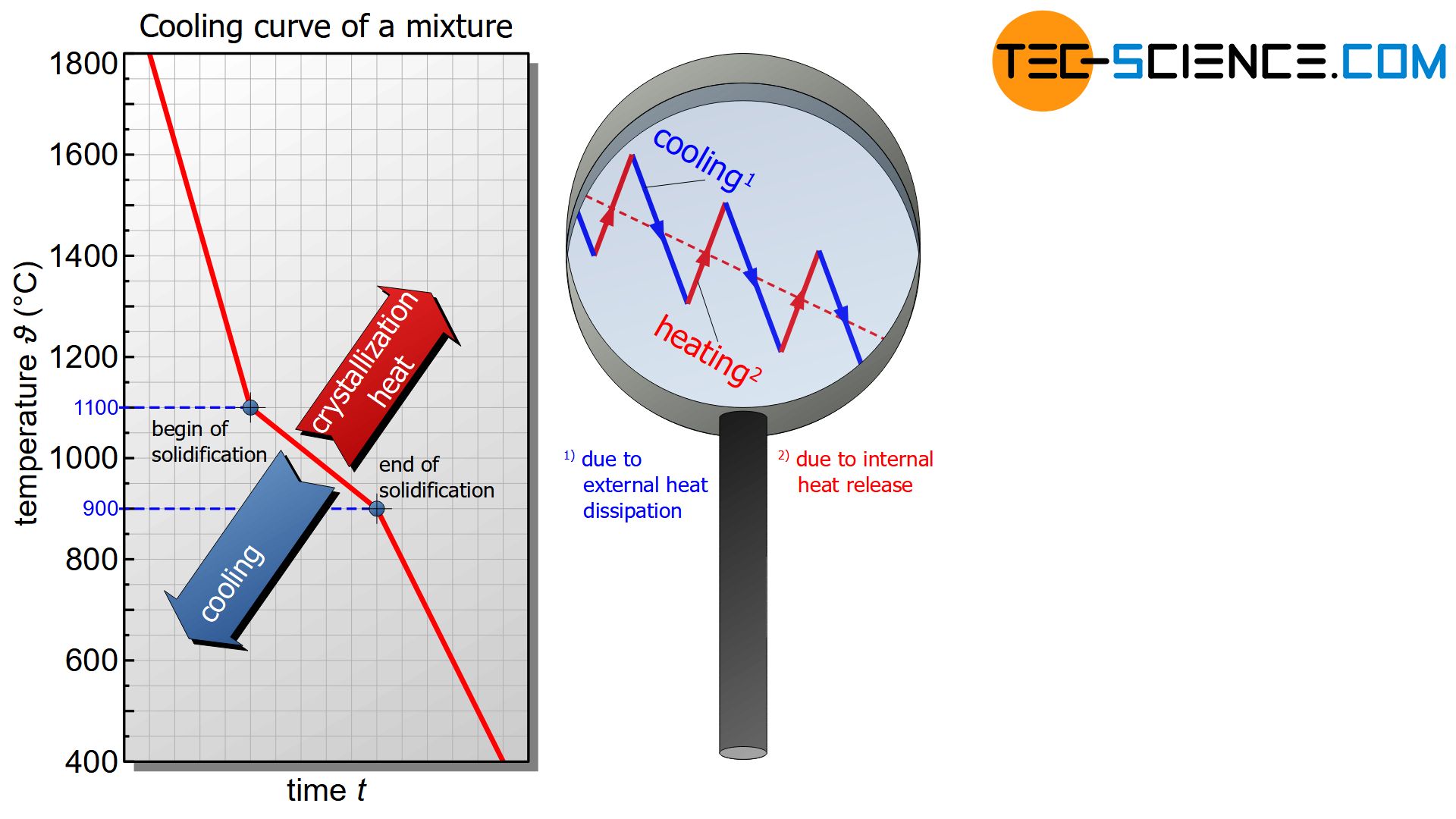 Figure: Cooling curve of a mixture of substances Figure: Cooling curve of a mixture of substances
In fact, there are also some alloys that have both, a thermal arrest as well as a flattend cooling curve (so-called solid solution alloys). Such alloy types are described in more detail in a separate article. NoteThe process of external heat dissipation and internal heat release during crystallization, which normally takes place simultaneously, is carried out separately in hand warmers due to undercooling. Because if the supercooled hand warmer is activated, it will not be cooled by an external heat dissipation at all in the first moment. Therefore, at first you only have the effect of internal heat release due to crystallization! Only when the hand warmer has become warm and firm does heat dissipation take place due to the temperature difference to the environment and it cools down slowly. In this case, internal heating and external cooling take place separately. |
【本文地址】
今日新闻 |
点击排行 |
|
推荐新闻 |
图片新闻 |
|
专题文章 |