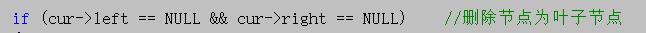| 二叉查找树(查找、插入、删除) | 您所在的位置:网站首页 › c删除函数 › 二叉查找树(查找、插入、删除) |
二叉查找树(查找、插入、删除)
|
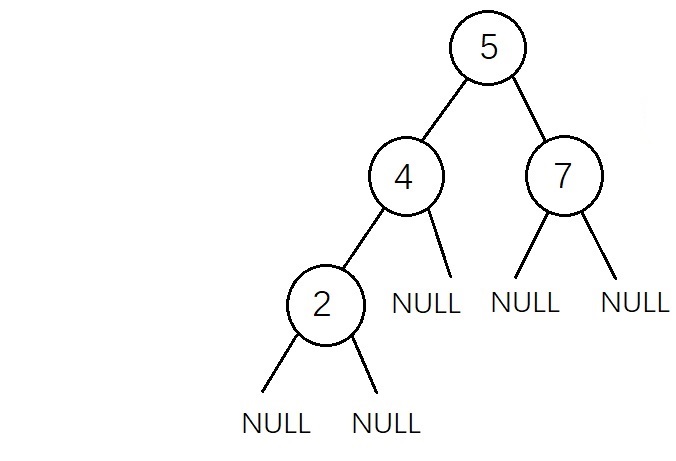
二叉查找树 二叉查找树(BST:Binary Search Tree)是一种特殊的二叉树,它改善了二叉树节点查找的效率。二叉查找树有以下性质: (1)若左子树不空,则左子树上所有节点的值均小于它的根节点的值 (2)若右子树不空,则右子树上所有节点的值均大于它的根节点的值 (3)左、右子树也分别为二叉排序树 (4)没有键值相等的节点
二叉查找树节点的定义: 1 typedef struct BSTreeNode 2 { 3 int data; 4 struct BSTreeNode *left;//左子树 5 struct BSTreeNode *right;//右子树 6 }BSTree;跟普通二叉树的节点定义相同 因为查找节点和插入节点都是在已经构建好二叉查找树的前提下才能进行的,在删除节点的时候才涉及到调整二叉树的操作,所以这里先以前序遍历的顺序直接输入一个二叉查找树,代码如下   1 /* 创建二叉查找树(数据以前序遍历顺序输入)*/
2 BSTree *Create_BSTreeNode(BSTree *nod)
3 {
4 int num;
5
6 scanf_s("%d", &num, 1);
7 if (num == 0) /* 假定输入的数据都为正数,以0作为NULL的标志 */
8 {
9 return NULL;
10 }
11 else
12 {
13 if ((nod = (BSTree *)malloc(sizeof(BSTree))) == NULL)
14 {
15 printf("内存空间不足");
16 exit(0);
17 }
18 nod->data = num;
19 nod->left = Create_BSTreeNode(nod->left);
20 nod->right = Create_BSTreeNode(nod->right);
21
22 return nod;
23 }
24 }
25
26 /* 前序遍历二叉树,并打印 */
27 void PreOrder_Traverse(BSTree *nod, int level)
28 {
29 if (nod == NULL)
30 {
31 return ;
32 }
33
34 printf("data = %d level = %d\n", nod->data, level);
35 PreOrder_Traverse(nod->left, level + 1);
36 PreOrder_Traverse(nod->right, level + 1);
37 }
View Code
1 /* 创建二叉查找树(数据以前序遍历顺序输入)*/
2 BSTree *Create_BSTreeNode(BSTree *nod)
3 {
4 int num;
5
6 scanf_s("%d", &num, 1);
7 if (num == 0) /* 假定输入的数据都为正数,以0作为NULL的标志 */
8 {
9 return NULL;
10 }
11 else
12 {
13 if ((nod = (BSTree *)malloc(sizeof(BSTree))) == NULL)
14 {
15 printf("内存空间不足");
16 exit(0);
17 }
18 nod->data = num;
19 nod->left = Create_BSTreeNode(nod->left);
20 nod->right = Create_BSTreeNode(nod->right);
21
22 return nod;
23 }
24 }
25
26 /* 前序遍历二叉树,并打印 */
27 void PreOrder_Traverse(BSTree *nod, int level)
28 {
29 if (nod == NULL)
30 {
31 return ;
32 }
33
34 printf("data = %d level = %d\n", nod->data, level);
35 PreOrder_Traverse(nod->left, level + 1);
36 PreOrder_Traverse(nod->right, level + 1);
37 }
View Code
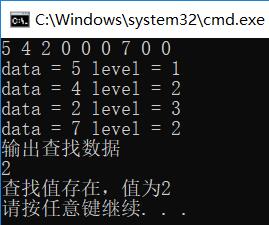
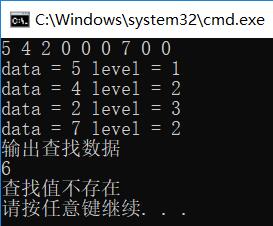
1、查找节点(递归实现) 若根结点的关键字等于查找的关键字,查找成功,若小于根结点的关键字的值,递归查找左子树,若大于根结点的关键字的值,递归查找右子树,若子树为空,则查找失败,查找的操作较为简单,实现代码如下 1 /* 查找特定值 */ 2 void SearchData(int targ, BSTree *nod) 3 { 4 if (nod != NULL) 5 { 6 if (nod->data == targ) 7 { 8 printf("查找值存在,值为%d\n", nod->data); 9 } 10 else if (nod->data > targ) 11 { 12 SearchData(targ, nod->left); //递归查找左子树 13 } 14 else if (nod->data right); //递归查找右子树 17 } 18 } 19 else if (nod == NULL) 20 { 21 printf("查找值不存在\n"); 22 } 23 }通过 BST 查找节点,理想情况下我们需要检查的节点数可以减半。如下图中的 BST 树,包含了 15 个节点。从根节点开始执行查找算法,第一次比较决定我们是移向左子树还是右子树,对于任意一种情况,一旦执行这一步,我们需要访问的节点数就减少了一半,从 15 降到了 7。同样,下一步访问的节点也减少了一半,从 7 降到了 3,以此类推,根据这一特点,查找算法的时间复杂度应该是 O(log2n)
(图片来源:https://www.cnblogs.com/gaochundong/p/binary_search_tree.html)
对于 BST 查找算法来说,其十分依赖于树中节点的拓扑结构,也就是节点间的布局关系,当 BST 树中的节点以扇形结构散开时,对它的插入、删除和查找操作最优的情况下可以达到亚线性的运行时间 O(log2n), 因为当在 BST 中查找一个节点时,每一步比较操作后都会将节点的数量减少一半。尽管如此,如果拓扑结构像下图中的样子时,运行时间就会退减到线性时间 O(n)。因为每一步比较操作后还是需要逐个比较其余的节点, 也就是说,在这种情况下,在 BST 中查找节点与在数组(Array)中查找就基本类似了。 因此,BST 算法查找时间依赖于树的拓扑结构。最佳情况是 O(log2n),而最坏情况是 O(n)
测试用例:
查找:以前序遍历顺序输入一个二叉查找树(0作为NULL标志)
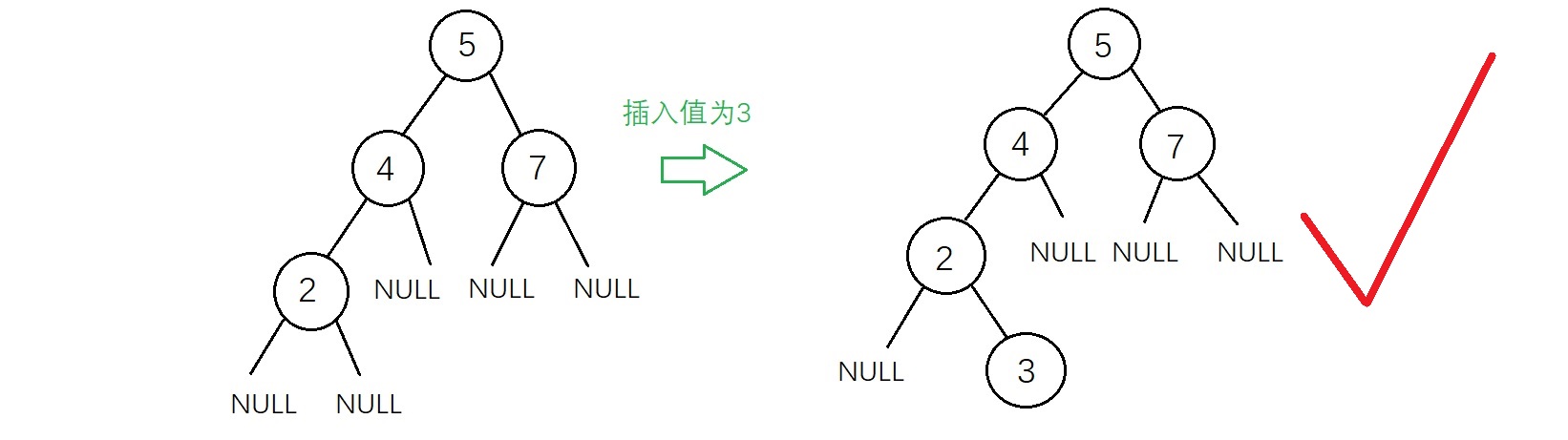
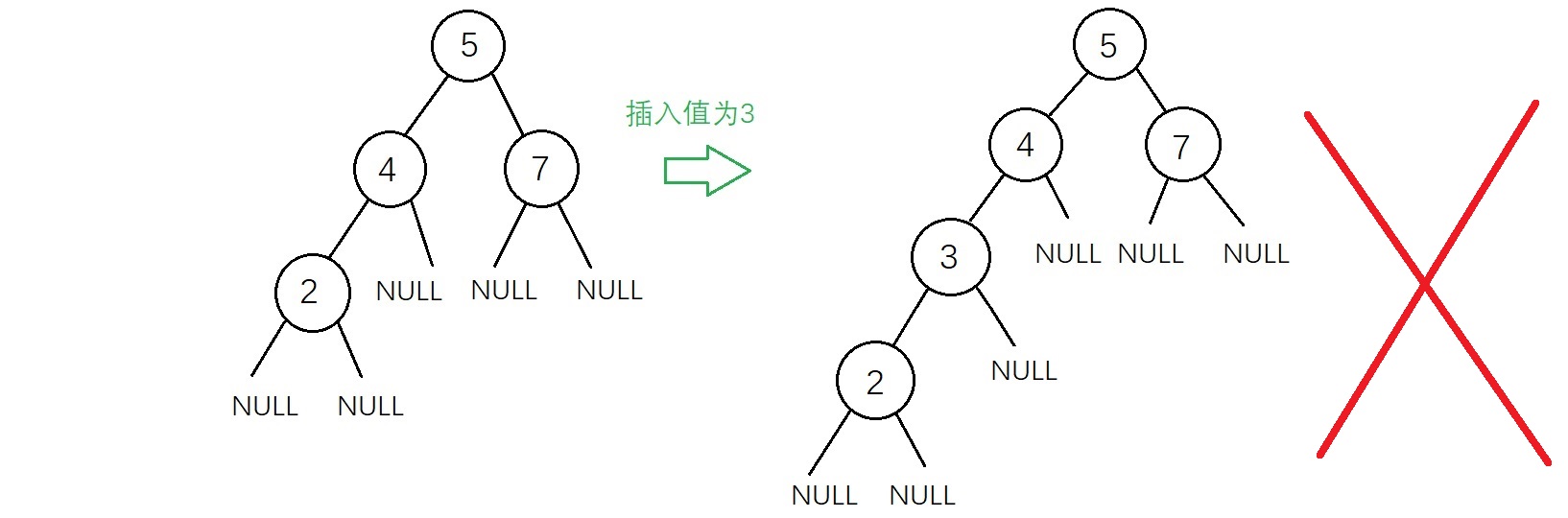
2、插入节点(递归实现) 新插入的结点一定是一个新添加的叶子结点,如下图
虽然上面两种插入结果得到的二叉树都符合二叉查找树的性质,但是不满足“新插入的结点一定是一个新添加的叶子结点”,因为有了这个特点插入的操作变得相对简单,实现代码如下 1 /* 添加新节点 */ 2 BSTree *AddNewNode(BSTree *cur, int NewData) 3 { 4 if (cur == NULL) 5 { 6 if ((cur = (BSTree *)malloc(sizeof(BSTree))) == NULL) //创建新节点 7 { 8 printf("内存不足"); 9 exit(0); 10 } 11 cur->data = NewData; 12 cur->left = NULL; 13 cur->right = NULL; 14 15 return cur; 16 } 17 if (NewData > cur->data) 18 { 19 cur->right = AddNewNode(cur->right, NewData); 20 } 21 else if (NewData < cur->data) 22 { 23 cur->left = AddNewNode(cur->left, NewData); 24 } 25 else if (NewData == cur->data) 26 { 27 printf("不允许插入重复值\n"); 28 exit(0); 29 } 30 31 return cur; 32 }
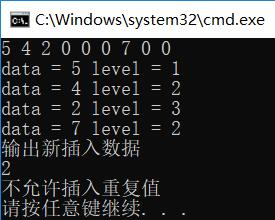
测试用例:
插入:以前序遍历顺序输入一个二叉查找树
3、删除节点 删除节点的操作相对查找和插入要相对复杂一些,主要考虑以下三种情况(前两种情况操作较为简单,第三种较为复杂)
在删除操作前先用要找到待删除节点的位置(这里使用的递归,也可以改成迭代)
情形一:删除叶子节点
因为删除叶子节点不会破坏BST的结构,删除叶子节点的操作较为简单,步骤如下 1、判断待删除节点的左右子树是否为空,如果都为空那么就是叶子节点
2、判断待删除节点是待删除节点父节点的右子树还是左子树,将对应的指针赋值NULL
3、free待删除节点
实现代码: 1 /* 删除节点 */ 2 /* cur为待删除节点, parent为待删除节点的父节点 */ 3 void DeletNode(BSTree *parent, BSTree *cur, int DelData) 4 { 5 BSTree *SNode = NULL; //后继节点 6 BSTree *PSNode = NULL; //后继节点的父节点 7 8 if (cur == NULL) 9 { 10 printf("删除节点不存在\n"); 11 exit(0); 12 } 13 else if (DelData > cur->data) 14 { 15 DeletNode(cur, cur->right, DelData); 16 } 17 else if (DelData < cur->data) 18 { 19 DeletNode(cur, cur->left, DelData); 20 } 21 else if(DelData == cur->data) 22 { 23 if (cur->left == NULL && cur->right == NULL) //待删除节点为叶子节点 24 { 25 if (parent->left == cur) //如果该节点是父节点的左子树 26 { 27 parent->left = NULL; 28 } 29 else if (parent->right == cur) //如果该节点是父节点的右子树 30 { 31 parent->right = NULL; 32 } 33 }因为删除节点这个子函数我是用的不带返回值的递归实现的,导致if else语句很多,后面我把删除节点这个子函数改成带返回值的递归,看起来要舒服不少,代码如下,有兴趣的读者可以看一下
  1 /* 删除节点 */
2 /* cur为待删除节点, parent为待删除节点的父节点 */
3 BSTree *DeletNode(BSTree *parent, BSTree *cur, int DelData)
4 {
5 BSTree *SNode = NULL; //后继节点
6 BSTree *PSNode = NULL; //后继节点的父节点
7 BSTree *temp = NULL; //临时保存待释放节点的子树,避免free后找不到左右子树
8
9 if (cur == NULL)
10 {
11 printf("删除节点不存在\n");
12 exit(0);
13 }
14 else if (DelData > cur->data)
15 {
16 cur->right = DeletNode(cur, cur->right, DelData);
17 }
18 else if (DelData < cur->data)
19 {
20 cur->left = DeletNode(cur, cur->left, DelData);
21 }
22 else if (DelData == cur->data)
23 {
24 if (cur->left == NULL && cur->right == NULL) //待删除节点为叶子节点
25 {
26 free(cur);
27 return NULL;
28 }
带返回值的递归实现
1 /* 删除节点 */
2 /* cur为待删除节点, parent为待删除节点的父节点 */
3 BSTree *DeletNode(BSTree *parent, BSTree *cur, int DelData)
4 {
5 BSTree *SNode = NULL; //后继节点
6 BSTree *PSNode = NULL; //后继节点的父节点
7 BSTree *temp = NULL; //临时保存待释放节点的子树,避免free后找不到左右子树
8
9 if (cur == NULL)
10 {
11 printf("删除节点不存在\n");
12 exit(0);
13 }
14 else if (DelData > cur->data)
15 {
16 cur->right = DeletNode(cur, cur->right, DelData);
17 }
18 else if (DelData < cur->data)
19 {
20 cur->left = DeletNode(cur, cur->left, DelData);
21 }
22 else if (DelData == cur->data)
23 {
24 if (cur->left == NULL && cur->right == NULL) //待删除节点为叶子节点
25 {
26 free(cur);
27 return NULL;
28 }
带返回值的递归实现
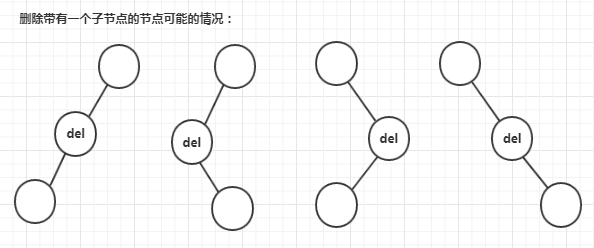
情形二:删除带有一个子节点的节点
(图片来源:https://www.cnblogs.com/songwenjie/p/8973217.html) 上图写了四种,但对待删除节点来说只有两种,只有左子树,或只有右子树,两种情况的处理方式基本相同,都是将待删除节点的左/右子树 赋值给 待删除节点的父节点的左/右子树
实现代码: 1 else if(cur->left != NULL && cur->right == NULL) //待删除节点只有左子树 2 { 3 if (parent->left == cur) 4 { 5 parent->left = cur->left; 6 } 7 else if (parent->right == cur) 8 { 9 parent->right = cur->left; 10 } 11 free(cur); //释放待删除节点 12 } 13 else if(cur->left == NULL && cur->right != NULL) //待删除节点只有右子树 14 { 15 if (parent->left == cur) 16 { 17 parent->left = cur->right; 18 } 19 else if (parent->right == cur) 20 { 21 parent->right = cur->right; 22 } 23 free(cur); //释放待删除节点 24 }
  1 else if(cur->left != NULL && cur->right == NULL) //待删除节点只有左子树
2 {
3 temp = cur->left;
4 free(cur);
5
6 return temp;;
7 }
8 else if(cur->left == NULL && cur->right != NULL) //待删除节点只有右子树
9 {
10 temp = cur->right;
11 free(cur);
12
13 return cur->right;
14 }
带返回值的递归实现
1 else if(cur->left != NULL && cur->right == NULL) //待删除节点只有左子树
2 {
3 temp = cur->left;
4 free(cur);
5
6 return temp;;
7 }
8 else if(cur->left == NULL && cur->right != NULL) //待删除节点只有右子树
9 {
10 temp = cur->right;
11 free(cur);
12
13 return cur->right;
14 }
带返回值的递归实现
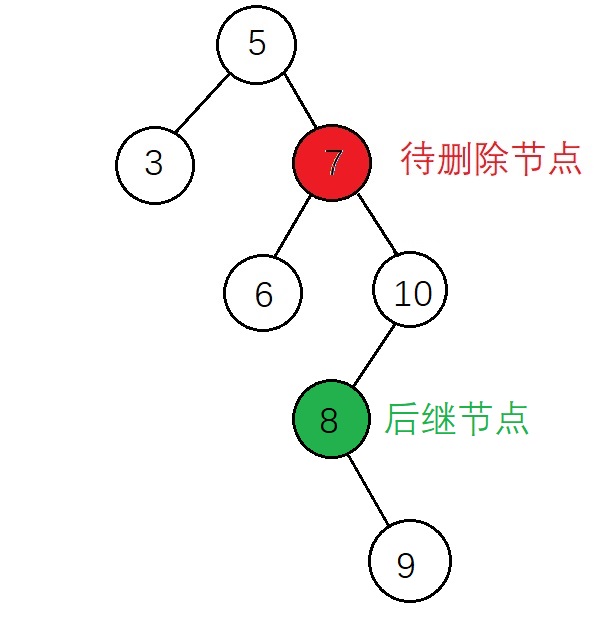
情形三:删除带两个节点的节点 因为删除节点会有破坏 BST 正确结构的风险,删除带两个节点的节点操作显得较为复杂,首先需要找到待删除节点的 后继节点 和 该后继节点的父节点,(一个节点的后继节点是指,这个节点在中序遍历序列中的下一个节点,相应的,前驱节点是指这个节点在中序遍历序列中的上一个节点),删除节点的后继节点一定是删除节点右子树的最左侧节点,这篇随笔采用的方式是后继节点替代待删除节点的方式而不是前驱节点替代删除节点,需要考虑的情况如下
1、后继节点为待删除节点的子节点 在后继节点为待删除节点的子节点的前提下,该后继节点有右子树和没有右子树的操作是相同的,都是将 后继节点 替代 待删除节点,并将待删除节点的左子树 赋值给 后继节点的左子树
实现代码: 1 else if(cur->left != NULL && cur->right != NULL) //待删除节点既有左子树也有右子树 2 { 3 SNode = SearchSuccessorNode(cur->right); //搜索后继节点 4 PSNode = SearchParentofSNode(cur->right, cur->right); //搜索后继节点的父节点 5 6 if (cur->right == SNode) //后继节点为待删除节点的右子树(后继节点有右子树和没有右子树的操作相同) 7 { 8 if (parent->left == cur) 9 { 10 parent->left = SNode; 11 SNode->left = cur->left; 12 13 free(cur); 14 } 15 else if (parent->right == cur) 16 { 17 parent->right = SNode; 18 SNode->left = cur->left; 19 20 free(cur); 21 } 22 }
  1 else if(cur->left != NULL && cur->right != NULL) //待删除节点既有左子树也有右子树
2 {
3 SNode = SearchSuccessorNode(cur->right); //搜索后继节点
4 PSNode = SearchParentofSNode(cur->right, cur->right); //搜索后继节点的父节点
5
6 if (cur->right == SNode) //后继节点为待删除节点的右子树(后继节点有右子树和没有右子树的操作相同)
7 {
8 SNode->left = cur->left;
9 free(cur);
10
11 return SNode;
12 }
带返回值的递归实现
1 else if(cur->left != NULL && cur->right != NULL) //待删除节点既有左子树也有右子树
2 {
3 SNode = SearchSuccessorNode(cur->right); //搜索后继节点
4 PSNode = SearchParentofSNode(cur->right, cur->right); //搜索后继节点的父节点
5
6 if (cur->right == SNode) //后继节点为待删除节点的右子树(后继节点有右子树和没有右子树的操作相同)
7 {
8 SNode->left = cur->left;
9 free(cur);
10
11 return SNode;
12 }
带返回值的递归实现
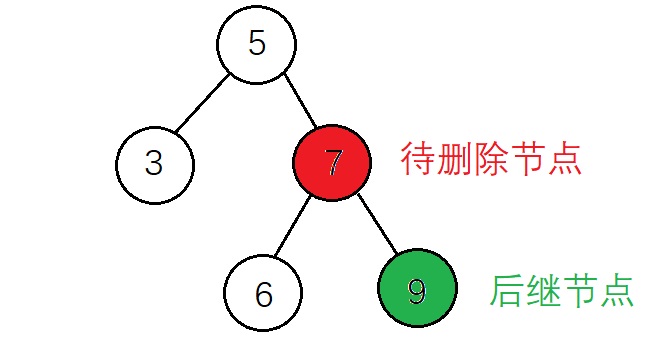
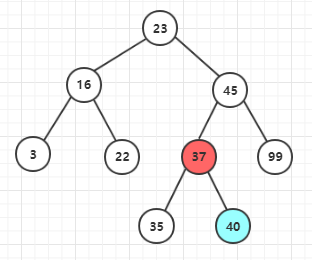
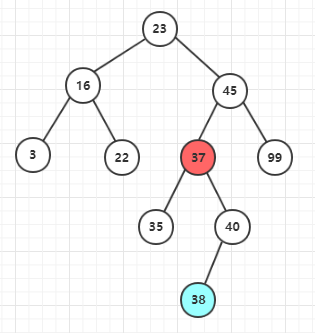
2、后继节点不为待删除节点的子节点 这里后继节点还要在分为后继节点有子节点和没有子节点的情况 (1)后继节点没有右子节点
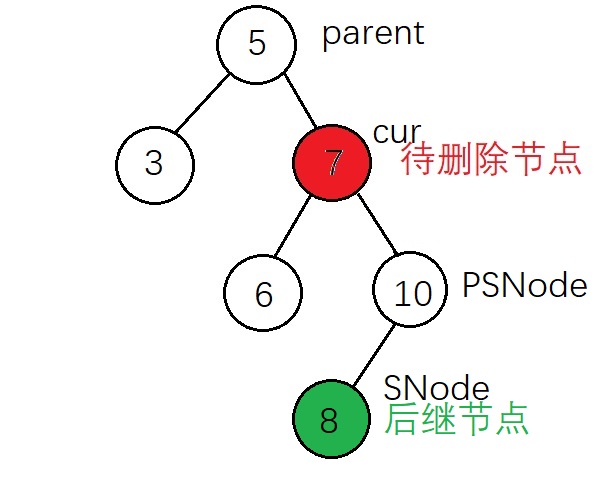
根据实现代码来标注上面的节点
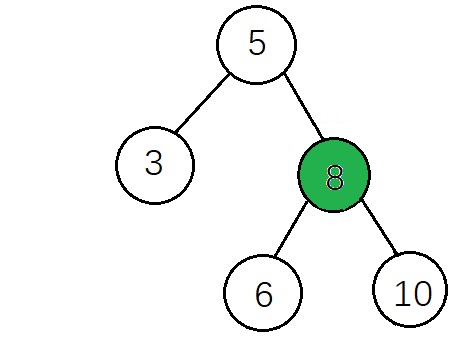
删除后:
实现代码: 1 else if (cur->right != SNode && SNode->right == NULL) //后继节点不为待删除节点的右子树,并且该后继节点没有右子树 2 { 3 if (parent->left == cur) 4 { 5 parent->left = SNode; 6 SNode->left = cur->left; 7 SNode->right = cur->right; 8 PSNode->left = NULL; 9 10 free(cur); 11 } 12 else if (parent->right == cur) 13 { 14 parent->right = SNode; 15 SNode->left = cur->left; 16 SNode->right = cur->right; 17 PSNode->left = NULL; 18 19 free(cur); 20 } 21 }
  1 else if (cur->right != SNode && SNode->right == NULL) //后继节点不为待删除节点的右子树,并且该后继节点没有右子树
2 {
3 SNode->left = cur->left;
4 SNode->right = cur->right;
5 PSNode->left = NULL;
6 free(cur);
7
8 return SNode;
9 }
带返回值的递归实现
1 else if (cur->right != SNode && SNode->right == NULL) //后继节点不为待删除节点的右子树,并且该后继节点没有右子树
2 {
3 SNode->left = cur->left;
4 SNode->right = cur->right;
5 PSNode->left = NULL;
6 free(cur);
7
8 return SNode;
9 }
带返回值的递归实现
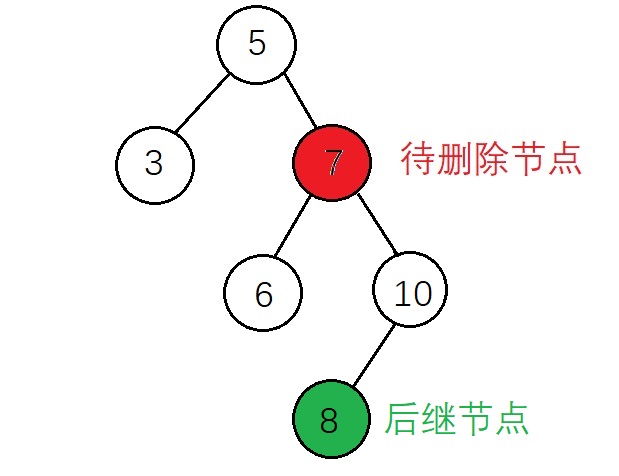
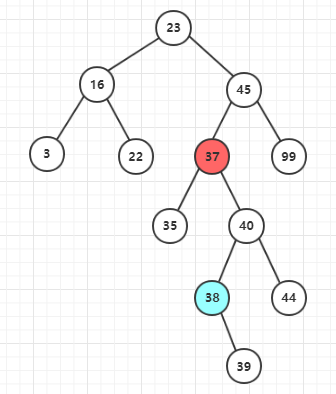
(2)后继节点有右子节点
删除后:
与上面的后继节点没有右子节点相比需要增加一个操作,需要将后继节点的右子树 赋值给 后继节点的父节点的左子树 实现代码: 1 else if (cur->right != SNode && SNode->right != NULL) //后继节点不为待删除节点的右子树,并且该后继节点有右子树 2 { 3 if (parent->left == cur) 4 { 5 parent->left = SNode; 6 PSNode->left = SNode->right; //后继节点的右子树作为后继节点父节点的左子树 7 SNode->left = cur->left; 8 SNode->right = cur->right; 9 10 free(cur); 11 } 12 else if (parent->right == cur) 13 { 14 parent->right = SNode; 15 PSNode->left = SNode->right; //后继节点的右子树作为后继节点父节点的左子树 16 SNode->left = cur->left; 17 SNode->right = cur->right; 18 19 free(cur); 20 } 21 }
  1 else if (cur->right != SNode && SNode->right != NULL) //后继节点不为待删除节点的右子树,并且该后继节点有右子树
2 {
3
4 PSNode->left = SNode->right; //后继节点的右子树作为后继节点父节点的左子树
5 SNode->left = cur->left;
6 SNode->right = cur->right;
7 free(cur);
8
9 return SNode;
10 }
带返回值的递归实现
1 else if (cur->right != SNode && SNode->right != NULL) //后继节点不为待删除节点的右子树,并且该后继节点有右子树
2 {
3
4 PSNode->left = SNode->right; //后继节点的右子树作为后继节点父节点的左子树
5 SNode->left = cur->left;
6 SNode->right = cur->right;
7 free(cur);
8
9 return SNode;
10 }
带返回值的递归实现
测试数据: 一、“后继节点是删除节点的子节点”(因为后继节点有无子树的操作相同,这里只测试没有子树的情况)
二、“后继节点不是删除节点的子节点,且后继节点没有右子树”
三、“后继节点不是删除节点的子节点,且后继节点有右子树”
完整代码:(注:对free(cur)的位置进行了调整)
  1 #include
2 #include
3 #include
4
5 #define LEFT 1
6 #define RIGHT 2
7
8 typedef struct BSTreeNode
9 {
10 int data;
11 struct BSTreeNode *left;//左子树
12 struct BSTreeNode *right;//右子树
13 }BSTree;
14
15 BSTree *Create_BSTreeNode(BSTree *nod); //创建二叉查找树
16 void PreOrder_Traverse(BSTree *nod, int level); //前序遍历二叉树,并打印
17 void SearchData(int targ, BSTree *nod); //查找特定值
18 BSTree *AddNewNode(BSTree *cur, int NewData); //添加新的节点
19 void DeletNode(BSTree *parent, BSTree *cur, int DelData); //删除节点
20 BSTree *SearchSuccessorNode(BSTree *nod); //搜索后继节点
21 BSTree *SearchParentofSNode(BSTree *Pnod, BSTree *nod); //搜索后继节点的父节点
22
23 int main()
24 {
25 BSTree *nod = NULL;
26 //int num;
27 int key;
28 //int del;
29
30 nod = Create_BSTreeNode(nod);
31 PreOrder_Traverse(nod, 1);
32
33 //printf("输出查找数据\n");
34 //scanf_s("%d", &num, 1);
35 //SearchData(num, nod);
36
37 printf("输出新插入数据\n");
38 scanf_s("%d", &key, 1);
39 nod = AddNewNode(nod, key);
40
41 //printf("输出删除的数据\n");
42 //scanf_s("%d", &del, 1);
43 //DeletNode(nod, nod, del);
44
45
46 PreOrder_Traverse(nod, 1);
47
48 return 0;
49 }
50
51 /* 搜索后继节点的父节点 */
52 BSTree *SearchParentofSNode(BSTree *Pnod, BSTree *nod)
53 {
54 while (1)
55 {
56 if (nod->left != NULL)
57 {
58 Pnod = nod;
59 nod = nod->left;
60 }
61 else
62 {
63 break;
64 }
65 }
66
67 return Pnod;
68 }
69
70 /* 搜索后继节点 */
71 BSTree *SearchSuccessorNode(BSTree *nod)
72 {
73 while (1)
74 {
75 if (nod->left != NULL)
76 {
77 nod = nod->left;
78 }
79 else
80 {
81 break;
82 }
83 }
84
85 return nod;
86 }
87
88 /* 删除节点 */
89 /* cur为待删除节点, parent为待删除节点的父节点 */
90 void DeletNode(BSTree *parent, BSTree *cur, int DelData)
91 {
92 BSTree *SNode = NULL; //后继节点
93 BSTree *PSNode = NULL; //后继节点的父节点
94
95 if (DelData > cur->data)
96 {
97 DeletNode(cur, cur->right, DelData);
98 }
99 else if (DelData < cur->data)
100 {
101 DeletNode(cur, cur->left, DelData);
102 }
103 else if(DelData == cur->data)
104 {
105 if (cur->left == NULL && cur->right == NULL) //待删除节点为叶子节点
106 {
107 if (parent->left == cur) //如果该节点是父节点的左子树
108 {
109 parent->left = NULL;
110 }
111 else if (parent->right == cur) //如果该节点是父节点的右子树
112 {
113 parent->right = NULL;
114 }
115 }
116 else if(cur->left != NULL && cur->right == NULL) //待删除节点只有左子树
117 {
118 if (parent->left == cur)
119 {
120 parent->left = cur->left;
121 }
122 else if (parent->right == cur)
123 {
124 parent->right = cur->left;
125 }
126 }
127 else if(cur->left == NULL && cur->right != NULL) //待删除节点只有右子树
128 {
129 if (parent->left == cur)
130 {
131 parent->left = cur->right;
132 }
133 else if (parent->right == cur)
134 {
135 parent->right = cur->right;
136 }
137 }
138 else if(cur->left != NULL && cur->right != NULL) //待删除节点既有左子树也有右子树
139 {
140 SNode = SearchSuccessorNode(cur->right); //搜索后继节点
141 PSNode = SearchParentofSNode(cur->right, cur->right); //搜索后继节点的父节点
142
143 if (cur->right == SNode) //后继节点为待删除节点的右子树(后继节点有右子树和没有右子树的操作相同)
144 {
145 if (parent->left == cur)
146 {
147 parent->left = SNode;
148 SNode->left = cur->left;
149 }
150 else if (parent->right == cur)
151 {
152 parent->right = SNode;
153 SNode->left = cur->left;
154 }
155 }
156 else if (cur->right != SNode && SNode->right == NULL) //后继节点不为待删除节点的右子树,并且该后继节点没有右子树
157 {
158 if (parent->left == cur)
159 {
160 parent->left = SNode;
161 SNode->left = cur->left;
162 SNode->right = cur->right;
163 PSNode->left = NULL;
164 }
165 else if (parent->right == cur)
166 {
167 parent->right = SNode;
168 SNode->left = cur->left;
169 SNode->right = cur->right;
170 PSNode->left = NULL;
171 }
172 }
173 else if (cur->right != SNode && SNode->right != NULL) //后继节点不为待删除节点的右子树,并且该后继节点有右子树
174 {
175 if (parent->left == cur)
176 {
177 parent->left = SNode;
178 PSNode->left = SNode->right; //后继节点的右子树作为后继节点父节点的左子树
179 SNode->left = cur->left;
180 SNode->right = cur->right;
181 }
182 else if (parent->right == cur)
183 {
184 parent->right = SNode;
185 PSNode->left = SNode->right; //后继节点的右子树作为后继节点父节点的左子树
186 SNode->left = cur->left;
187 SNode->right = cur->right;
188 }
189 }
190 }
191 free(cur); //释放待删除节点
192 }
193 }
194
195 /* 添加新节点 */
196 BSTree *AddNewNode(BSTree *cur, int NewData)
197 {
198 if (cur == NULL)
199 {
200 if ((cur = (BSTree *)malloc(sizeof(BSTree))) == NULL) //创建新节点
201 {
202 printf("内存不足");
203 exit(0);
204 }
205 cur->data = NewData;
206 cur->left = NULL;
207 cur->right = NULL;
208
209 return cur;
210 }
211 if (NewData > cur->data)
212 {
213 cur->right = AddNewNode(cur->right, NewData);
214 }
215 else if (NewData < cur->data)
216 {
217 cur->left = AddNewNode(cur->left, NewData);
218 }
219 else if (NewData == cur->data)
220 {
221 printf("不允许插入重复值\n");
222 exit(0);
223 }
224
225 return cur;
226 }
227
228 /* 查找特定值 */
229 void SearchData(int targ, BSTree *nod)
230 {
231 if (nod != NULL)
232 {
233 if (nod->data == targ)
234 {
235 printf("查找值存在,值为%d\n", nod->data);
236 }
237 else if (nod->data > targ)
238 {
239 SearchData(targ, nod->left); //递归查找左子树
240 }
241 else if (nod->data right); //递归查找右子树
244 }
245 }
246 else if (nod == NULL)
247 {
248 printf("查找值不存在\n");
249 }
250 }
251
252 /* 创建二叉查找树(数据以前序遍历顺序输入)*/
253 BSTree *Create_BSTreeNode(BSTree *nod)
254 {
255 int num;
256
257 scanf_s("%d", &num, 1);
258 if (num == 0) /* 假定输入的数据都为正数,以0作为NULL的标志 */
259 {
260 return NULL;
261 }
262 else
263 {
264 if ((nod = (BSTree *)malloc(sizeof(BSTree))) == NULL)
265 {
266 printf("内存空间不足");
267 exit(0);
268 }
269 nod->data = num;
270 nod->left = Create_BSTreeNode(nod->left);
271 nod->right = Create_BSTreeNode(nod->right);
272
273 return nod;
274 }
275 }
276
277 /* 前序遍历二叉树,并打印 */
278 void PreOrder_Traverse(BSTree *nod, int level)
279 {
280 if (nod == NULL)
281 {
282 return ;
283 }
284
285 printf("data = %d level = %d\n", nod->data, level);
286 PreOrder_Traverse(nod->left, level + 1);
287 PreOrder_Traverse(nod->right, level + 1);
288 }
View Code
1 #include
2 #include
3 #include
4
5 #define LEFT 1
6 #define RIGHT 2
7
8 typedef struct BSTreeNode
9 {
10 int data;
11 struct BSTreeNode *left;//左子树
12 struct BSTreeNode *right;//右子树
13 }BSTree;
14
15 BSTree *Create_BSTreeNode(BSTree *nod); //创建二叉查找树
16 void PreOrder_Traverse(BSTree *nod, int level); //前序遍历二叉树,并打印
17 void SearchData(int targ, BSTree *nod); //查找特定值
18 BSTree *AddNewNode(BSTree *cur, int NewData); //添加新的节点
19 void DeletNode(BSTree *parent, BSTree *cur, int DelData); //删除节点
20 BSTree *SearchSuccessorNode(BSTree *nod); //搜索后继节点
21 BSTree *SearchParentofSNode(BSTree *Pnod, BSTree *nod); //搜索后继节点的父节点
22
23 int main()
24 {
25 BSTree *nod = NULL;
26 //int num;
27 int key;
28 //int del;
29
30 nod = Create_BSTreeNode(nod);
31 PreOrder_Traverse(nod, 1);
32
33 //printf("输出查找数据\n");
34 //scanf_s("%d", &num, 1);
35 //SearchData(num, nod);
36
37 printf("输出新插入数据\n");
38 scanf_s("%d", &key, 1);
39 nod = AddNewNode(nod, key);
40
41 //printf("输出删除的数据\n");
42 //scanf_s("%d", &del, 1);
43 //DeletNode(nod, nod, del);
44
45
46 PreOrder_Traverse(nod, 1);
47
48 return 0;
49 }
50
51 /* 搜索后继节点的父节点 */
52 BSTree *SearchParentofSNode(BSTree *Pnod, BSTree *nod)
53 {
54 while (1)
55 {
56 if (nod->left != NULL)
57 {
58 Pnod = nod;
59 nod = nod->left;
60 }
61 else
62 {
63 break;
64 }
65 }
66
67 return Pnod;
68 }
69
70 /* 搜索后继节点 */
71 BSTree *SearchSuccessorNode(BSTree *nod)
72 {
73 while (1)
74 {
75 if (nod->left != NULL)
76 {
77 nod = nod->left;
78 }
79 else
80 {
81 break;
82 }
83 }
84
85 return nod;
86 }
87
88 /* 删除节点 */
89 /* cur为待删除节点, parent为待删除节点的父节点 */
90 void DeletNode(BSTree *parent, BSTree *cur, int DelData)
91 {
92 BSTree *SNode = NULL; //后继节点
93 BSTree *PSNode = NULL; //后继节点的父节点
94
95 if (DelData > cur->data)
96 {
97 DeletNode(cur, cur->right, DelData);
98 }
99 else if (DelData < cur->data)
100 {
101 DeletNode(cur, cur->left, DelData);
102 }
103 else if(DelData == cur->data)
104 {
105 if (cur->left == NULL && cur->right == NULL) //待删除节点为叶子节点
106 {
107 if (parent->left == cur) //如果该节点是父节点的左子树
108 {
109 parent->left = NULL;
110 }
111 else if (parent->right == cur) //如果该节点是父节点的右子树
112 {
113 parent->right = NULL;
114 }
115 }
116 else if(cur->left != NULL && cur->right == NULL) //待删除节点只有左子树
117 {
118 if (parent->left == cur)
119 {
120 parent->left = cur->left;
121 }
122 else if (parent->right == cur)
123 {
124 parent->right = cur->left;
125 }
126 }
127 else if(cur->left == NULL && cur->right != NULL) //待删除节点只有右子树
128 {
129 if (parent->left == cur)
130 {
131 parent->left = cur->right;
132 }
133 else if (parent->right == cur)
134 {
135 parent->right = cur->right;
136 }
137 }
138 else if(cur->left != NULL && cur->right != NULL) //待删除节点既有左子树也有右子树
139 {
140 SNode = SearchSuccessorNode(cur->right); //搜索后继节点
141 PSNode = SearchParentofSNode(cur->right, cur->right); //搜索后继节点的父节点
142
143 if (cur->right == SNode) //后继节点为待删除节点的右子树(后继节点有右子树和没有右子树的操作相同)
144 {
145 if (parent->left == cur)
146 {
147 parent->left = SNode;
148 SNode->left = cur->left;
149 }
150 else if (parent->right == cur)
151 {
152 parent->right = SNode;
153 SNode->left = cur->left;
154 }
155 }
156 else if (cur->right != SNode && SNode->right == NULL) //后继节点不为待删除节点的右子树,并且该后继节点没有右子树
157 {
158 if (parent->left == cur)
159 {
160 parent->left = SNode;
161 SNode->left = cur->left;
162 SNode->right = cur->right;
163 PSNode->left = NULL;
164 }
165 else if (parent->right == cur)
166 {
167 parent->right = SNode;
168 SNode->left = cur->left;
169 SNode->right = cur->right;
170 PSNode->left = NULL;
171 }
172 }
173 else if (cur->right != SNode && SNode->right != NULL) //后继节点不为待删除节点的右子树,并且该后继节点有右子树
174 {
175 if (parent->left == cur)
176 {
177 parent->left = SNode;
178 PSNode->left = SNode->right; //后继节点的右子树作为后继节点父节点的左子树
179 SNode->left = cur->left;
180 SNode->right = cur->right;
181 }
182 else if (parent->right == cur)
183 {
184 parent->right = SNode;
185 PSNode->left = SNode->right; //后继节点的右子树作为后继节点父节点的左子树
186 SNode->left = cur->left;
187 SNode->right = cur->right;
188 }
189 }
190 }
191 free(cur); //释放待删除节点
192 }
193 }
194
195 /* 添加新节点 */
196 BSTree *AddNewNode(BSTree *cur, int NewData)
197 {
198 if (cur == NULL)
199 {
200 if ((cur = (BSTree *)malloc(sizeof(BSTree))) == NULL) //创建新节点
201 {
202 printf("内存不足");
203 exit(0);
204 }
205 cur->data = NewData;
206 cur->left = NULL;
207 cur->right = NULL;
208
209 return cur;
210 }
211 if (NewData > cur->data)
212 {
213 cur->right = AddNewNode(cur->right, NewData);
214 }
215 else if (NewData < cur->data)
216 {
217 cur->left = AddNewNode(cur->left, NewData);
218 }
219 else if (NewData == cur->data)
220 {
221 printf("不允许插入重复值\n");
222 exit(0);
223 }
224
225 return cur;
226 }
227
228 /* 查找特定值 */
229 void SearchData(int targ, BSTree *nod)
230 {
231 if (nod != NULL)
232 {
233 if (nod->data == targ)
234 {
235 printf("查找值存在,值为%d\n", nod->data);
236 }
237 else if (nod->data > targ)
238 {
239 SearchData(targ, nod->left); //递归查找左子树
240 }
241 else if (nod->data right); //递归查找右子树
244 }
245 }
246 else if (nod == NULL)
247 {
248 printf("查找值不存在\n");
249 }
250 }
251
252 /* 创建二叉查找树(数据以前序遍历顺序输入)*/
253 BSTree *Create_BSTreeNode(BSTree *nod)
254 {
255 int num;
256
257 scanf_s("%d", &num, 1);
258 if (num == 0) /* 假定输入的数据都为正数,以0作为NULL的标志 */
259 {
260 return NULL;
261 }
262 else
263 {
264 if ((nod = (BSTree *)malloc(sizeof(BSTree))) == NULL)
265 {
266 printf("内存空间不足");
267 exit(0);
268 }
269 nod->data = num;
270 nod->left = Create_BSTreeNode(nod->left);
271 nod->right = Create_BSTreeNode(nod->right);
272
273 return nod;
274 }
275 }
276
277 /* 前序遍历二叉树,并打印 */
278 void PreOrder_Traverse(BSTree *nod, int level)
279 {
280 if (nod == NULL)
281 {
282 return ;
283 }
284
285 printf("data = %d level = %d\n", nod->data, level);
286 PreOrder_Traverse(nod->left, level + 1);
287 PreOrder_Traverse(nod->right, level + 1);
288 }
View Code
因为主要是分析二叉查找树的查找、插入、删除操作,没有考虑二叉树为空 或 待删除节点为根节点的情况
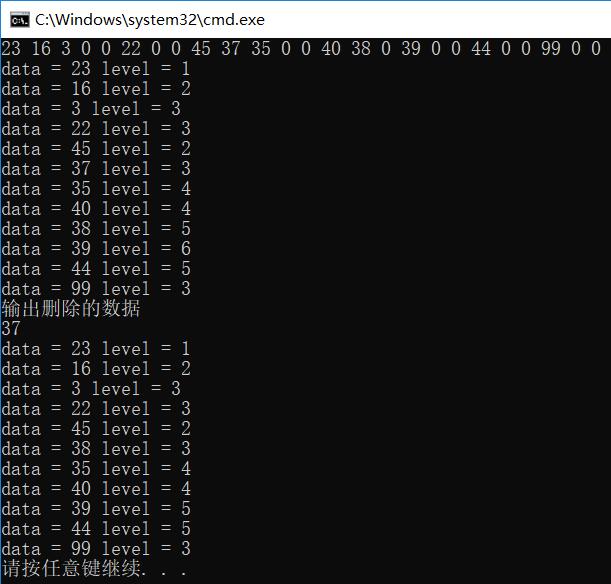
补充:(注:删除节点函数修改成了带返回值的递归实现——更新日期2019/8/13)   1 #include
2 #include
3 #include
4
5 #define LEFT 1
6 #define RIGHT 2
7
8 typedef struct BSTreeNode
9 {
10 int data;
11 struct BSTreeNode *left;//左子树
12 struct BSTreeNode *right;//右子树
13 }BSTree;
14
15 BSTree *Create_BSTreeNode(BSTree *nod); //创建二叉查找树
16 void PreOrder_Traverse(BSTree *nod, int level); //前序遍历二叉树,并打印
17 void SearchData(int targ, BSTree *nod); //查找特定值
18 BSTree *AddNewNode(BSTree *cur, int NewData); //添加新的节点
19 BSTree *DeletNode(BSTree *parent, BSTree *cur, int DelData); //删除节点
20 BSTree *SearchSuccessorNode(BSTree *nod); //搜索后继节点
21 BSTree *SearchParentofSNode(BSTree *Pnod, BSTree *nod); //搜索后继节点的父节点
22
23 int main()
24 {
25 BSTree *nod = NULL;
26 //int num;
27 //int key;
28 int del;
29
30 nod = Create_BSTreeNode(nod);
31 PreOrder_Traverse(nod, 1);
32
33 /*printf("输出查找数据\n");
34 scanf_s("%d", &num, 1);
35 SearchData(num, nod);*/
36
37 /*printf("输出新插入数据\n");
38 scanf_s("%d", &key, 1);
39 nod = AddNewNode(nod, key);*/
40
41 printf("输出删除的数据\n");
42 scanf_s("%d", &del, 1);
43 nod = DeletNode(nod, nod, del);
44
45
46 PreOrder_Traverse(nod, 1);
47
48 return 0;
49 }
50
51 /* 搜索后继节点的父节点 */
52 BSTree *SearchParentofSNode(BSTree *Pnod, BSTree *nod)
53 {
54 while (1)
55 {
56 if (nod->left != NULL)
57 {
58 Pnod = nod;
59 nod = nod->left;
60 }
61 else
62 {
63 break;
64 }
65 }
66
67 return Pnod;
68 }
69
70 /* 搜索后继节点 */
71 BSTree *SearchSuccessorNode(BSTree *nod)
72 {
73 while (1)
74 {
75 if (nod->left != NULL)
76 {
77 nod = nod->left;
78 }
79 else
80 {
81 break;
82 }
83 }
84
85 return nod;
86 }
87
88 /* 删除节点 */
89 /* cur为待删除节点, parent为待删除节点的父节点 */
90 BSTree *DeletNode(BSTree *parent, BSTree *cur, int DelData)
91 {
92 BSTree *SNode = NULL; //后继节点
93 BSTree *PSNode = NULL; //后继节点的父节点
94 BSTree *temp = NULL; //临时保存待释放节点的子树,避免free后找不到左右子树
95
96 if (cur == NULL)
97 {
98 printf("删除节点不存在\n");
99 exit(0);
100 }
101 else if (DelData > cur->data)
102 {
103 cur->right = DeletNode(cur, cur->right, DelData);
104 }
105 else if (DelData < cur->data)
106 {
107 cur->left = DeletNode(cur, cur->left, DelData);
108 }
109 else if (DelData == cur->data)
110 {
111 if (cur->left == NULL && cur->right == NULL) //待删除节点为叶子节点
112 {
113 free(cur);
114 return NULL;
115 }
116 else if(cur->left != NULL && cur->right == NULL) //待删除节点只有左子树
117 {
118 temp = cur->left;
119 free(cur);
120
121 return temp;;
122 }
123 else if(cur->left == NULL && cur->right != NULL) //待删除节点只有右子树
124 {
125 temp = cur->right;
126 free(cur);
127
128 return cur->right;
129 }
130 else if(cur->left != NULL && cur->right != NULL) //待删除节点既有左子树也有右子树
131 {
132 SNode = SearchSuccessorNode(cur->right); //搜索后继节点
133 PSNode = SearchParentofSNode(cur->right, cur->right); //搜索后继节点的父节点
134
135 if (cur->right == SNode) //后继节点为待删除节点的右子树(后继节点有右子树和没有右子树的操作相同)
136 {
137 SNode->left = cur->left;
138 free(cur);
139
140 return SNode;
141 }
142 else if (cur->right != SNode && SNode->right == NULL) //后继节点不为待删除节点的右子树,并且该后继节点没有右子树
143 {
144 SNode->left = cur->left;
145 SNode->right = cur->right;
146 PSNode->left = NULL;
147 free(cur);
148
149 return SNode;
150 }
151 else if (cur->right != SNode && SNode->right != NULL) //后继节点不为待删除节点的右子树,并且该后继节点有右子树
152 {
153
154 PSNode->left = SNode->right; //后继节点的右子树作为后继节点父节点的左子树
155 SNode->left = cur->left;
156 SNode->right = cur->right;
157 free(cur);
158
159 return SNode;
160 }
161 }
162 }
163
164 return cur;
165 }
166
167 /* 添加新节点 */
168 BSTree *AddNewNode(BSTree *cur, int NewData)
169 {
170 if (cur == NULL)
171 {
172 if ((cur = (BSTree *)malloc(sizeof(BSTree))) == NULL) //创建新节点
173 {
174 printf("内存不足");
175 exit(0);
176 }
177 cur->data = NewData;
178 cur->left = NULL;
179 cur->right = NULL;
180
181 return cur;
182 }
183 if (NewData > cur->data)
184 {
185 cur->right = AddNewNode(cur->right, NewData);
186 }
187 else if (NewData < cur->data)
188 {
189 cur->left = AddNewNode(cur->left, NewData);
190 }
191 else if (NewData == cur->data)
192 {
193 printf("不允许插入重复值\n");
194 exit(0);
195 }
196
197 return cur;
198 }
199
200 /* 查找特定值 */
201 void SearchData(int targ, BSTree *nod)
202 {
203 if (nod != NULL)
204 {
205 if (nod->data == targ)
206 {
207 printf("查找值存在,值为%d\n", nod->data);
208 }
209 else if (nod->data > targ)
210 {
211 SearchData(targ, nod->left); //递归查找左子树
212 }
213 else if (nod->data right); //递归查找右子树
216 }
217 }
218 else if (nod == NULL)
219 {
220 printf("查找值不存在\n");
221 }
222 }
223
224 /* 创建二叉查找树(数据以前序遍历顺序输入)*/
225 BSTree *Create_BSTreeNode(BSTree *nod)
226 {
227 int num;
228
229 scanf_s("%d", &num, 1);
230 if (num == 0) /* 假定输入的数据都为正数,以0作为NULL的标志 */
231 {
232 return NULL;
233 }
234 else
235 {
236 if ((nod = (BSTree *)malloc(sizeof(BSTree))) == NULL)
237 {
238 printf("内存空间不足");
239 exit(0);
240 }
241 nod->data = num;
242 nod->left = Create_BSTreeNode(nod->left);
243 nod->right = Create_BSTreeNode(nod->right);
244
245 return nod;
246 }
247 }
248
249 /* 前序遍历二叉树,并打印 */
250 void PreOrder_Traverse(BSTree *nod, int level)
251 {
252 if (nod == NULL)
253 {
254 return ;
255 }
256
257 printf("data = %d level = %d\n", nod->data, level);
258 PreOrder_Traverse(nod->left, level + 1);
259 PreOrder_Traverse(nod->right, level + 1);
260 }
View Code
1 #include
2 #include
3 #include
4
5 #define LEFT 1
6 #define RIGHT 2
7
8 typedef struct BSTreeNode
9 {
10 int data;
11 struct BSTreeNode *left;//左子树
12 struct BSTreeNode *right;//右子树
13 }BSTree;
14
15 BSTree *Create_BSTreeNode(BSTree *nod); //创建二叉查找树
16 void PreOrder_Traverse(BSTree *nod, int level); //前序遍历二叉树,并打印
17 void SearchData(int targ, BSTree *nod); //查找特定值
18 BSTree *AddNewNode(BSTree *cur, int NewData); //添加新的节点
19 BSTree *DeletNode(BSTree *parent, BSTree *cur, int DelData); //删除节点
20 BSTree *SearchSuccessorNode(BSTree *nod); //搜索后继节点
21 BSTree *SearchParentofSNode(BSTree *Pnod, BSTree *nod); //搜索后继节点的父节点
22
23 int main()
24 {
25 BSTree *nod = NULL;
26 //int num;
27 //int key;
28 int del;
29
30 nod = Create_BSTreeNode(nod);
31 PreOrder_Traverse(nod, 1);
32
33 /*printf("输出查找数据\n");
34 scanf_s("%d", &num, 1);
35 SearchData(num, nod);*/
36
37 /*printf("输出新插入数据\n");
38 scanf_s("%d", &key, 1);
39 nod = AddNewNode(nod, key);*/
40
41 printf("输出删除的数据\n");
42 scanf_s("%d", &del, 1);
43 nod = DeletNode(nod, nod, del);
44
45
46 PreOrder_Traverse(nod, 1);
47
48 return 0;
49 }
50
51 /* 搜索后继节点的父节点 */
52 BSTree *SearchParentofSNode(BSTree *Pnod, BSTree *nod)
53 {
54 while (1)
55 {
56 if (nod->left != NULL)
57 {
58 Pnod = nod;
59 nod = nod->left;
60 }
61 else
62 {
63 break;
64 }
65 }
66
67 return Pnod;
68 }
69
70 /* 搜索后继节点 */
71 BSTree *SearchSuccessorNode(BSTree *nod)
72 {
73 while (1)
74 {
75 if (nod->left != NULL)
76 {
77 nod = nod->left;
78 }
79 else
80 {
81 break;
82 }
83 }
84
85 return nod;
86 }
87
88 /* 删除节点 */
89 /* cur为待删除节点, parent为待删除节点的父节点 */
90 BSTree *DeletNode(BSTree *parent, BSTree *cur, int DelData)
91 {
92 BSTree *SNode = NULL; //后继节点
93 BSTree *PSNode = NULL; //后继节点的父节点
94 BSTree *temp = NULL; //临时保存待释放节点的子树,避免free后找不到左右子树
95
96 if (cur == NULL)
97 {
98 printf("删除节点不存在\n");
99 exit(0);
100 }
101 else if (DelData > cur->data)
102 {
103 cur->right = DeletNode(cur, cur->right, DelData);
104 }
105 else if (DelData < cur->data)
106 {
107 cur->left = DeletNode(cur, cur->left, DelData);
108 }
109 else if (DelData == cur->data)
110 {
111 if (cur->left == NULL && cur->right == NULL) //待删除节点为叶子节点
112 {
113 free(cur);
114 return NULL;
115 }
116 else if(cur->left != NULL && cur->right == NULL) //待删除节点只有左子树
117 {
118 temp = cur->left;
119 free(cur);
120
121 return temp;;
122 }
123 else if(cur->left == NULL && cur->right != NULL) //待删除节点只有右子树
124 {
125 temp = cur->right;
126 free(cur);
127
128 return cur->right;
129 }
130 else if(cur->left != NULL && cur->right != NULL) //待删除节点既有左子树也有右子树
131 {
132 SNode = SearchSuccessorNode(cur->right); //搜索后继节点
133 PSNode = SearchParentofSNode(cur->right, cur->right); //搜索后继节点的父节点
134
135 if (cur->right == SNode) //后继节点为待删除节点的右子树(后继节点有右子树和没有右子树的操作相同)
136 {
137 SNode->left = cur->left;
138 free(cur);
139
140 return SNode;
141 }
142 else if (cur->right != SNode && SNode->right == NULL) //后继节点不为待删除节点的右子树,并且该后继节点没有右子树
143 {
144 SNode->left = cur->left;
145 SNode->right = cur->right;
146 PSNode->left = NULL;
147 free(cur);
148
149 return SNode;
150 }
151 else if (cur->right != SNode && SNode->right != NULL) //后继节点不为待删除节点的右子树,并且该后继节点有右子树
152 {
153
154 PSNode->left = SNode->right; //后继节点的右子树作为后继节点父节点的左子树
155 SNode->left = cur->left;
156 SNode->right = cur->right;
157 free(cur);
158
159 return SNode;
160 }
161 }
162 }
163
164 return cur;
165 }
166
167 /* 添加新节点 */
168 BSTree *AddNewNode(BSTree *cur, int NewData)
169 {
170 if (cur == NULL)
171 {
172 if ((cur = (BSTree *)malloc(sizeof(BSTree))) == NULL) //创建新节点
173 {
174 printf("内存不足");
175 exit(0);
176 }
177 cur->data = NewData;
178 cur->left = NULL;
179 cur->right = NULL;
180
181 return cur;
182 }
183 if (NewData > cur->data)
184 {
185 cur->right = AddNewNode(cur->right, NewData);
186 }
187 else if (NewData < cur->data)
188 {
189 cur->left = AddNewNode(cur->left, NewData);
190 }
191 else if (NewData == cur->data)
192 {
193 printf("不允许插入重复值\n");
194 exit(0);
195 }
196
197 return cur;
198 }
199
200 /* 查找特定值 */
201 void SearchData(int targ, BSTree *nod)
202 {
203 if (nod != NULL)
204 {
205 if (nod->data == targ)
206 {
207 printf("查找值存在,值为%d\n", nod->data);
208 }
209 else if (nod->data > targ)
210 {
211 SearchData(targ, nod->left); //递归查找左子树
212 }
213 else if (nod->data right); //递归查找右子树
216 }
217 }
218 else if (nod == NULL)
219 {
220 printf("查找值不存在\n");
221 }
222 }
223
224 /* 创建二叉查找树(数据以前序遍历顺序输入)*/
225 BSTree *Create_BSTreeNode(BSTree *nod)
226 {
227 int num;
228
229 scanf_s("%d", &num, 1);
230 if (num == 0) /* 假定输入的数据都为正数,以0作为NULL的标志 */
231 {
232 return NULL;
233 }
234 else
235 {
236 if ((nod = (BSTree *)malloc(sizeof(BSTree))) == NULL)
237 {
238 printf("内存空间不足");
239 exit(0);
240 }
241 nod->data = num;
242 nod->left = Create_BSTreeNode(nod->left);
243 nod->right = Create_BSTreeNode(nod->right);
244
245 return nod;
246 }
247 }
248
249 /* 前序遍历二叉树,并打印 */
250 void PreOrder_Traverse(BSTree *nod, int level)
251 {
252 if (nod == NULL)
253 {
254 return ;
255 }
256
257 printf("data = %d level = %d\n", nod->data, level);
258 PreOrder_Traverse(nod->left, level + 1);
259 PreOrder_Traverse(nod->right, level + 1);
260 }
View Code
|
【本文地址】